Ghana is home to over 27 million people. Agriculture contributes around 30% of the GDP and employs half of the working population. 80% of agricultural production occurs in small farmer operations averaging 1.2 hectares in size. One of the country’s major problems is pronounced socio-economic North-South inequality and is the starting point of many development projects and strategies. Maize is Ghana‘s most important grain and the second most important staple crop (after cassava). Maize production is the main source of income for a majority of smallholder farmer households. Other important crops in terms of production area and volume include cocoa, yams and plantain. Cocoa is the main export crop followed by cashew, while rice dominates imports. The national diet is heavily reliant on starchy staples, which has contributed to a recent increase in rates of overweight and obesity (more than half of women in the Greater Accra region are overweight or obese), with rates of micronutrient deficiencies remaining high.
Read the full country dossier here, and read the country innovation study on the status of agricultural innovations, innovation platforms and innovation investments in Ghana here.
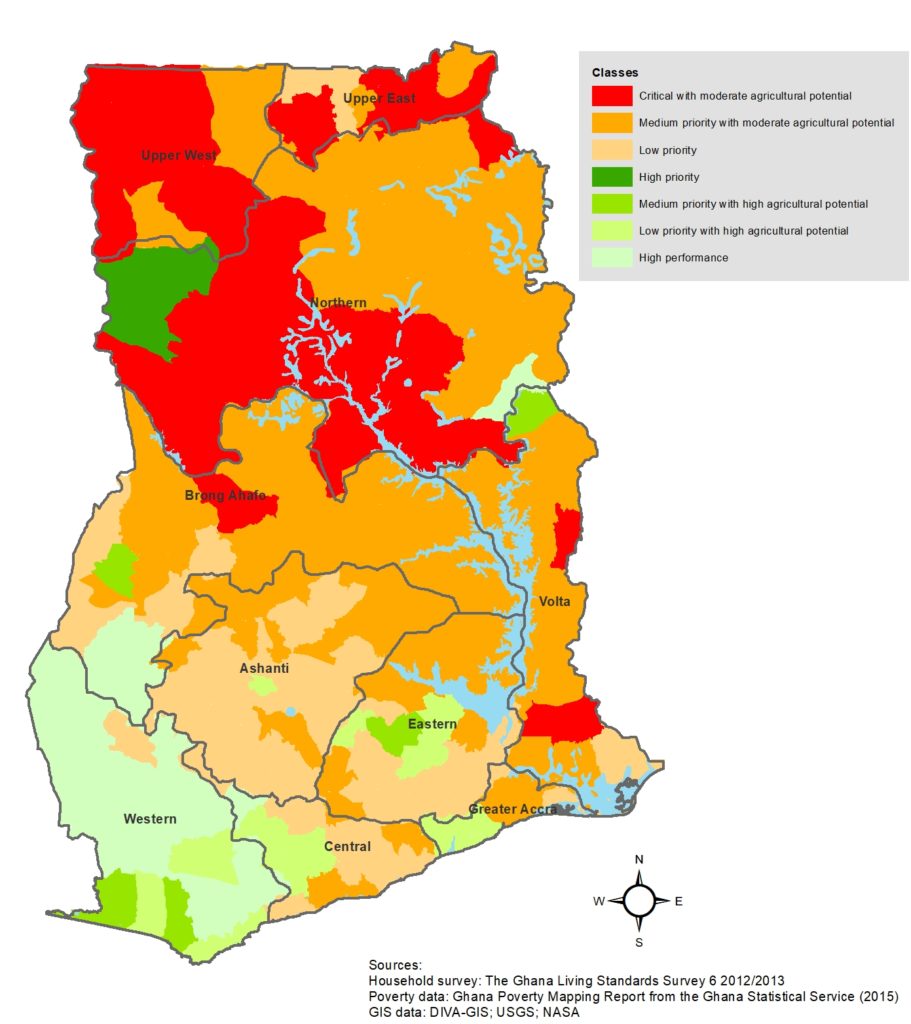
Agricultural Typology of Ghana: